Tooth wear is a lesion of a dental tissue, not related to caries.
It can be:
- attrition;
- abrasion;
- tooth wear;
- stressful lesion of the neck of the tooth;
- erosion
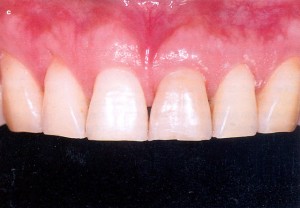
Maxillary frontal teeth wear

Strongly expressed wear maxillary frontal teeth
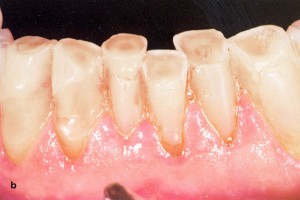
Strongly expressed wear of mandibular frontal teeth
Attrition – it‘s physiological wear of hard tissues, occurring due to tooth-to-tooth contact, especially when there are parafunctions (the disturbed or distorted function of organ or organ systems). Tooth-to-tooth contacts occur when swallowing food, talking, lifting heavy objects, in stressful situations. In this process, by-products are not involved. Dental attrition increasingly damages the teeth of young people. Research results show that dental attrition is typical to 60 percent of people.
Longevity of the teeth is determined by how long teeth are in contact with each other during normal function. Any other tooth-to-tooth contact, except eating, is called bruxism. It’s the main reason behind dental attrition in humans.
what is bruxism?
During the normal function, teeth are occluded only while chewing and swallowing. In the dormant state, a small gap remains between teeth, even thou the lips are sealed.
Bruxism – meaningless masticatory movements, caused by rapid contractions of muscles and strong clenching of the jaw. At that time, due to attrition of top and bottom teeth lines attrition to each other, an unpleasant, creaky sound is heard. Mostly it occurs during sleep. This condition is attributed to parafunctions (the disturbed or distorted function of organ or organ systems). Bruxism is an unconscious behavior. It was determined that the teeth of people with symptoms of bruxism contact with each other seven times more often than those of healthy people. Nighttime bruxism can be brief but very intense.
Symptoms of bruxism may occur in 5 to 20 percent of people, 5 percent may have persistent symptoms of bruxism. Incorrect occlusion, which forms when the tooth grows in a wrong way, also if teeth are of irregular shape, could also be a reason for which bruxism may occur. If a person’s diet is not wholesome or is the absorption of nutrients is not functioning correctly, a deficiency of critically essential vitamins and minerals, such as magnesium, B group vitamins and other, occurs. Bruxism may occur if the person has nervous and endocrine system diseases if there are lesions of the cerebral cortex or brainstem (epilepsy, tumors). Undoubtedly, psychological factors play a critically important role. These are various stresses, nervous tension. Personality type of person is also a significant reason for which teeth grinding may occur. It usually happens to susceptible, scrupulous people. Very animated children who get lots of emotions during the day can also do teeth grinding at night. Teeth grinding can be like a response to pain, for example, when extraordinarily sick or during injuries. Incorrectly placed fillings, dental crowns can provoke bruxism. When taking antidepressants, cases of bruxism may also occur.
Apart from nocturnal bruxism there also is daytime bruxism. It’s typical for people to clench teeth during psychological tension. Perhaps you have noticed that if stronger anxiety occurs or when concentrating intensely, working intensively, person’s muscles of mastication located in the area of the lower jaw and temples are contracting; however, the person doesn’t feel that his teeth are tightly clenched.
If bruxism continues for a longer time, the negative impact on the system of organs of the oral cavity is inevitable. Accelerated wearing of teeth, dentures, and fillings occurs. Their fractures, breakages are possible. Tooth mobility may increase, pain may occur in the area of the temporomandibular joint, jaw movement may get disturbed; also spasms and pains in muscles of mastication may be felt, especially in areas of their attachment. When the teeth are clenched involuntary, mucosa of the cheeks is also clenched, it can be injured, and bite marks can be seen clearly. Imprints in the mucosa of cheeks and tongue appear because when the teeth are kept clenched for a long time, less space left in the oral cavity. Cheeks and especially tongue tightly presses towards teeth and interdental space. If bruxism is present along with the loss of molars, due to alterations developed in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), a clicking sound in the joint appears which can be heard by the person itself and those around. If the necessary prophylaxis measures aren’t taken, in three years blocking of TMJ movement can occur.
Teeth wearing the degree of each person is individual and mostly depends on the patient’s age. As people’s lifespan lengthens, the time of teeth life cycle also increases, therefore, as time goes by, the teeth are increasingly affected by the external forces, which causes them to wear more. Degree and scales of attrition significantly depend on the peculiarities of a person’s diet, occlusion, jaw muscles and habits of mastication.
Dental attrition is classified as follows:
0 – healthy enamel;
1 – shiny flat enamel, dentine is intact;
2 – dentine is exposed;
3 – a significant loss of masticatory surfaces.
Primary indications for restoring treatment would be:
- the patient feels that the present condition of teeth is unacceptable;
- due to lesions of dental tissues, the normal function of the teeth is disturbed and/or teeth sensitivity is present, and the application of conservative treatment measures cannot eliminate it.
- Teeth attrition is further progressing and can cause pulpal necrosis and/or dental restoration becomes problematic.
Treatment:
- Regular fixed dentures;
- Onlay, inlay;
- Fillings (adhesive restoration);
- Dental guards (occlusal splints), placed on teeth for the night, to prevent tooth-to-tooth contact. The guard splints the teeth and distribute the load evenly.
- Psychologist’s assistance could be useful in more severe cases.
Abrasion – loss of hard tissues of teeth, occurring due to mechanical impact, i.e., constant use of foreign objects that come into contact with the teeth. For instance, pipe smoking, chewing of hard objects (pencil, metal objects), vigorous toothbrushing, use of abrasive kinds of toothpaste/powder. Incorrect or too intense brushing of teeth is the main factor, due to which lesions in the area of the tooth neck occur. Professional abrasion may occur due to the presence of abrasive dust in the work environment, bad habits: nail-biting, propensity to bite the thread with teeth or fishing line. However, currently, this for abrasion is rarely encountered.
Tooth wear – defines the loss of hard tissues of the teeth due to the mastication of food. Abrasion of food usually determines the wearing of dental tissues. Usually, chewing off teeth is a physiological process. Pathological wearing occurs when hard and abrasive food is continuously chewed, for example, nuts. The abrasiveness of the food also influences wearing degree, as well as “softened” dental surfaces due to the consumption of fermented products. Big muscles of mastication and consumption of unprocessed food products are also of influence.
Stressful lesion of the neck of the tooth – a chronic gradual pathological loss of hard tissues in the area where the dental crown passes to the root.
One of the theories on the lesion of the neck of the tooth, it is thought that during the movement of the lower jaw, the masticatory load causes the bending of the tooth. Due to this, fractures form in the enamel which causes the loss of enamel and dentine as time passes. Such lesions can be isolated, or several adjacent teeth can also have lesions. As dental fractures appear in the neck area, it becomes less resistant to abrasions and erosions. Clear, angular, wedge-shaped defects are typical to such lesions. Sometimes the lesion can be located beneath the gums.
Lesions present in the area of the neck of the tooth not always require restoration, unless when toot sensitivity or defect is in the aesthetic zone. In the case of parafunction, therapeutic measures which would stabilize the occlusion and equally distribute the masticatory load, are necessary. Correct toothbrushing technique is needed.
Erosion (dental erosion) – a slow, nearly painless loss of hard dental tissue caused by acids or chelation impact. Microorganisms have no influence here. This is the main difference between caries.
The working environment can be a reason for dental erosion when the air at the workplace is acidic due to entering vapors of acids, swimming pool water with acidic pH in which people swim for many years. Quite often, food is the cause of dental erosion, when large quantities of tomatoes, apples, sauerkraut, cucumbers, citrus fruits are consumed, also when large amounts of fruit juices are consumed, which are far more destructive than fruits, especially when cooled. Altogether, drinking copious quantities of fruit juices is the most widespread cause of dental erosion. Frequent sucking of vitamin C or drinking of various drinks, sucking candy containing vitamin C causes dental erosion. Aspirin also causes dental erosion, especially if chewed. Its relevant to elderly persons, who use aspirin to reduce blood clotting, and relieve long-term pain. It’s described that dental erosion can be caused by a habit of eating pizza often, especially under aggravating circumstances like pregnancy or anemia. Teeth whitening can also be the cause of dental erosion, especially when trays with bleaching agents are left on teeth for evening or night time. Brushing teeth after every meal is also a harmful habit.


