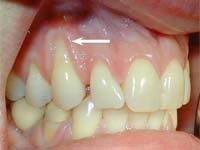
Gingival (gum) recession – a condition when due to receding gums, the surface of the dental root gets gradually exposed.
Causes:
- Recession due to mechanical irritation, usually because of traumatizing toothbrushing;
- Recession due to inflammation caused by the local plaque (typical in the area of protruding teeth, where the bone, covering the root surface is thin);
- Recession due to the dissemination of destructive periodontal disease;
- Too short frenulum of lips, cheeks, and tongue. When the tissues move, they pull the gums and traumatize them;
- After orthodontal treatment (tooth displacement, dental arch expansion);
- Recession due to the harmful habit of keeping sharp objects in the mouth.
Symptoms:
- A toothache,
- Changes in gum consistency,
- Changes in color of gums,
- Tooth sensitivity in the cervical area,
- The exposed surface of the dental roots,
- Receding edge of the gums.
Recessions are classified by depth as follows:
- shallow (3 mm),
- average (3-5mm)
- deep (deeper than 5mm).
By depth recessions are classified as follows:
- Narrow (up to 3mm)
- Wide (more than 3mm).
Treatment of gingival recession:
Aesthetic complaints, increased sensitivity of dental roots, root surface caries, tooth neck abrasion, impeded personal oral hygiene in that area are the main indications. In the treatment of recession, patient’s cooperation is critically important – correct, oral hygiene and elimination of harmful habits allows to expect for the treatment to be successful.
Treatment objective – to stop or reduce the recession of gums, and, if possible, to restore their former contour.
If the gum recession is not substantial, and provoking factors are identified and eliminated, the progress of the disease is stopped.
Conservative treatment:
- Training of correct personal oral hygiene,
- Removal of dental plaque and tartar,
- Orthodontal treatment – straightening of the incorrectly positioned teeth.
Surgical treatment is applied when the conservative means cannot help, and recession progresses. In such cases, the exposed roots are covered by transferring or pushing the flaps of healthy gums from the adjacent areas of the oral cavity. Also, surgical loosening of the frenulum of lips, cheeks, and tongue can be performed.